
Electric Vehicles 101
Everything you need to know about electric vehicles. Your journey to electric starts here.
The Power of Battery-Powered
The battery is the heart of an EV. It stores energy (measured in kilowatt-hours or kWh) and powers the motor. Modern EV batteries are designed to last 10-20 years or more with minimal degradation.
EV Ownership
Charger Basics
Charger Basics
Plug into a standard 120V wall outlet at home. Great for overnight charging but slower.
Uses a 240V/up to 80A connection for faster charging at home, work, or public locations. Utilizes J-1772 or NACS charging plugs. Charging speed up to 19.2kw.
Found at PowerUp stations, these fast chargers most commonly utilize CCS and NACS charging heads to provide rapid charging, perfect for on the go. Charging speeds up to 400kw



Common EV Questions
Most EVs can recharge in 30-45 minutes at a typical 150kW fast charger. However, PowerUp is delivering the fastest charge on the market, cutting this time in half with chargers capable of up to 400kW, getting you back on the road faster than ever.
We understand the concern about range anxiety, which is why PowerUp is committed to building a comprehensive network of fast chargers. This extensive coverage helps ensure that you’re never far from a charging point. Additionally, EVs typically come with navigation systems that can help you plan routes based on available charging stations, and our stations are easy to locate using various apps.
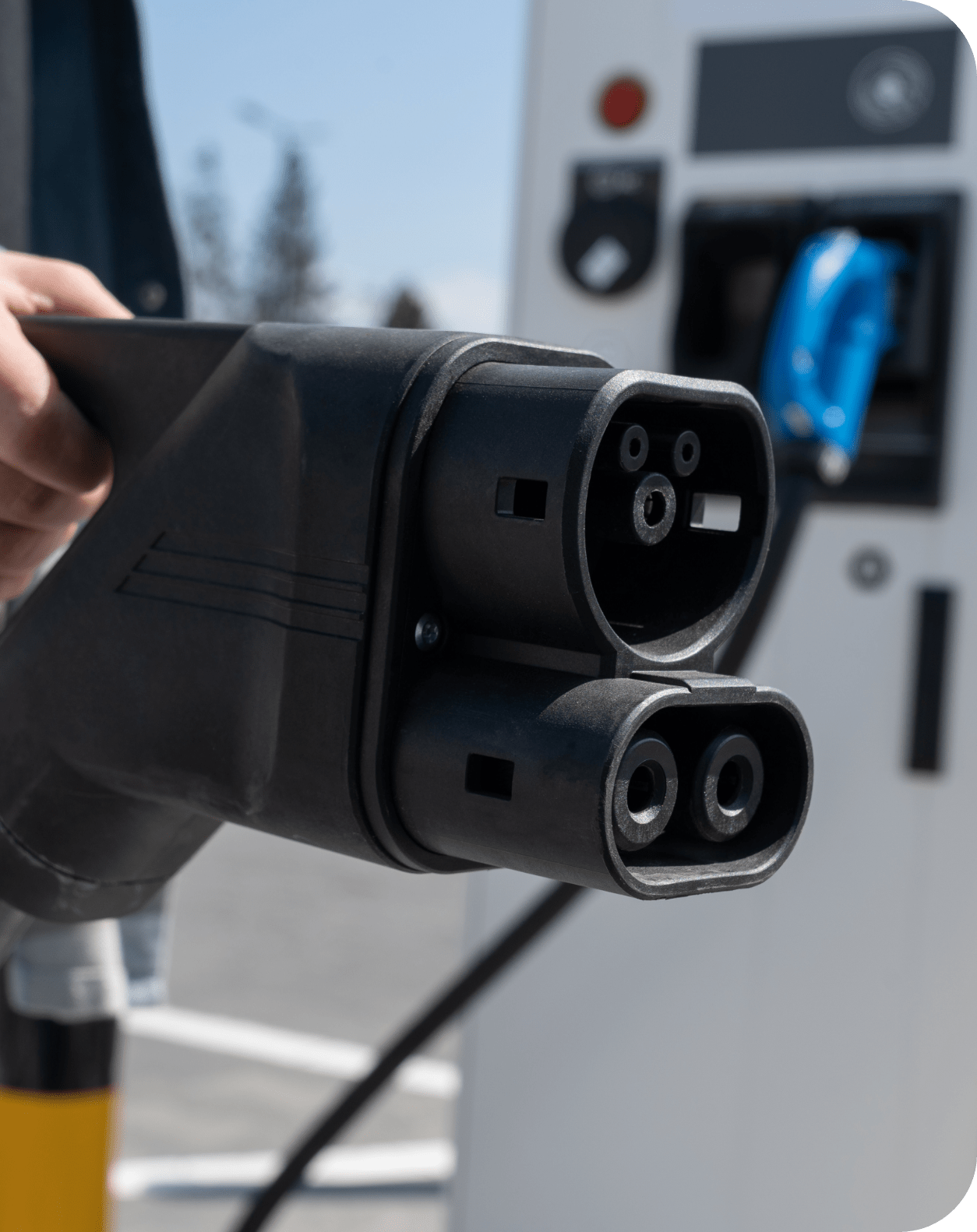
EVs use three main connector types for DCFC: CCS, NACS (Tesla), and CHAdeMO. Most charging stations support only one type, but PowerUp ensures compatibility by offering both NACS and CCS at every location, covering 98% of EVs on the road for a seamless charging experience.
Coming soon!
Electric Vehicle Glossary
Charging Connector/Plug
The physical plug connecting the charger to the EV (e.g., Type 1, Type 2, CCS, Tesla NACS).
CCS (Combined Charging System)
A fast-charging standard combining AC and DC pins. Widely used in North America and Europe for DC fast charging (e.g., CCS1 in the US, CCS2 in Europe). All our stations have CCS and NACS.
NACS (North American Charging Standard)
Tesla’s proprietary charging connector, now adopted by many automakers for AC and DC charging in North America. All our stations have CCS and NACS.
CHAdeMO
A DC fast-charging standard, primarily used by some Japanese EVs (e.g., Nissan Leaf). Less common globally but still supported at many stations. As of today, we will not be offering as Nissan has announced they will be changing this connector.
J1772 (SAE J1772)
A standard connector for Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging in North America. Also called a Type 1 connector.
Charging Adapter
A device that allows EVs with one charging connector type to use stations with a different standard. Common adapters include NACS-to-CCS, CCS-to-NACS, and others that bridge compatibility between different EV and charger manufacturers. These adapters enable broader charging access across networks.
AC Charging (Alternating Current)
Charging an EV using alternating current, typically slower, used in Level 1 and Level 2 chargers. Common for home and workplace charging.
DC Fast Charging (Direct Current)
High-power charging delivering DC directly to the EV’s battery, bypassing the onboard converter. Used for rapid charging (e.g., 50–350 kW).
Level 1 Charging
Slow charging using a standard 120V household outlet (1–2 kW). Typically adds 3–5 miles of range per hour.
Level 2 Charging
Faster AC charging using a 240V outlet or station (3.3–19.2 kW). Common for home, workplace, or public charging, adding 10–60 miles per hour.
Level 3 Charging
Another term for DC fast charging, delivering high power (50–350 kW) for rapid charging, often along highways. Also known as DCFC (Direct Current Fast Charger)
Charging Rate
The speed at which an EV charges, measured in kilowatts (kW). Higher kW (e.g., 150 kW vs. 50 kW) means faster charging.
mi/kWh (Miles per Kilowatt-Hour)
A measure of how efficiently an EV uses electricity, indicating how many miles it can travel on one kilowatt-hour of energy. Higher values mean greater efficiency (e.g., 4 mi/kWh is more efficient than 3 mi/kWh). Most of our Lightnings get between 2.1 mi/kWh to 2.4 mi/kWh for reference. 131 kW battery X (2.1 or 2.4) = 275.1 to 314.4 miles of range.
Range Per Hour (RPH)
The distance an EV can travel based on the energy added per hour of charging (e.g., 25 miles RPH for a Level 2 charger).
State of Charge (SoC)
The battery’s charge level, expressed as a percentage (e.g., 80% SoC means the battery is 80% full).
Charge Point Operator (CPO)
A company managing and maintaining EV charging stations, often providing access via apps or RFID cards. Your friendly neighborhood PowerUp is one of these.
Destination Charging
Charging stations at locations like hotels or malls, typically Level 2, for longer dwell times.
Dynamic Power Sharing
A technology used in EV charging systems, such as those at PowerUp Sites, that intelligently distributes available power across multiple chargers in real-time. For example, an 800 kW system can allocate 200 kW to each of four vehicles or 400 kW to two, optimizing charging efficiency based on vehicle needs and system capacity. This ensures a flexible, reliable, and efficient charging experience.
EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment)
The hardware (charger) that supplies electric power to an EV, including cables and connectors.
ICE Hole
A slang term for a person who parks a gas-powered (internal combustion engine) vehicle in an EV charging space, blocking access for EV drivers. Derived from the term ICEing, this behavior is considered rude and disruptive.
ICEing (Internal Combustion Engine blocking)
When a gas-powered vehicle parks in a spot designated for EV charging, preventing EV drivers from accessing the charger. This practice is considered inconsiderate and can hinder charging access.
Cutting the Cord
A slang term for unplugging another person’s EV from a charging station without permission. This act is considered disrespectful and can interrupt charging sessions, potentially stranding drivers who need a full charge.
Onboard Charger
The EV’s internal system converting AC to DC for battery charging. Its capacity (e.g., 11.5 kW or 19.2 kW) limits AC charging speed.
Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP)
A standard allowing communication between charging stations and management systems for interoperability.
Smart Charging
Charging systems that optimize energy use, often via apps, to reduce costs or balance grid demand (e.g., charging during off-peak hours).
Tesla Supercharger
Tesla’s proprietary DC fast-charging network, using NACS connectors, now opening to non-Tesla EVs in some regions.
Type 1 Connector
See J1772. Used for AC charging in North America.
Type 2 Connector
A standard AC charging connector used in Europe and other regions, also compatible with some DC charging setups.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
A hybrid vehicle with a rechargeable battery that can be charged via a plug, offering limited electric-only range.
kW (Kilowatt)
Unit of power indicating charging speed. Higher kW chargers (e.g., 150 kW) charge faster than lower ones (e.g., 7 kW).
kWh (Kilowatt-hour)
Unit of energy measuring battery capacity or energy delivered during charging. A 60 kWh battery can store 60 kilowatts for one hour.
Amp (Ampere)
Unit of electrical current. Higher amps deliver more power, speeding up charging (e.g., 32A vs. 16A chargers).
Volt (Voltage)
Unit of electrical potential. EV charging typically uses 120V (Level 1), 240V (Level 2), or 400–800V (DC fast charging).
V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid)
Technology allowing EVs to send stored energy back to the grid, supporting energy demand or stability.
V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything)
A broad term for technologies enabling an EV to communicate or transfer energy with various systems, including the grid (V2G), homes (V2H), buildings (V2B), or other vehicles (V2V), enhancing flexibility, energy management, and connectivity.
VPP (Virtual Power Plant)
A network of distributed energy resources—like EVs, solar panels, batteries, and smart appliances—coordinated through software to function as a single power plant. VPPs can supply energy to the grid, reduce demand, and improve grid reliability.
Partnership with Universities and Technical Schools
PowerUp is collaborating with leading universities and technical schools to drive innovation, develop cutting-edge EV technologies, and empower the next generation of talent in sustainable mobility. Interested in partnering?

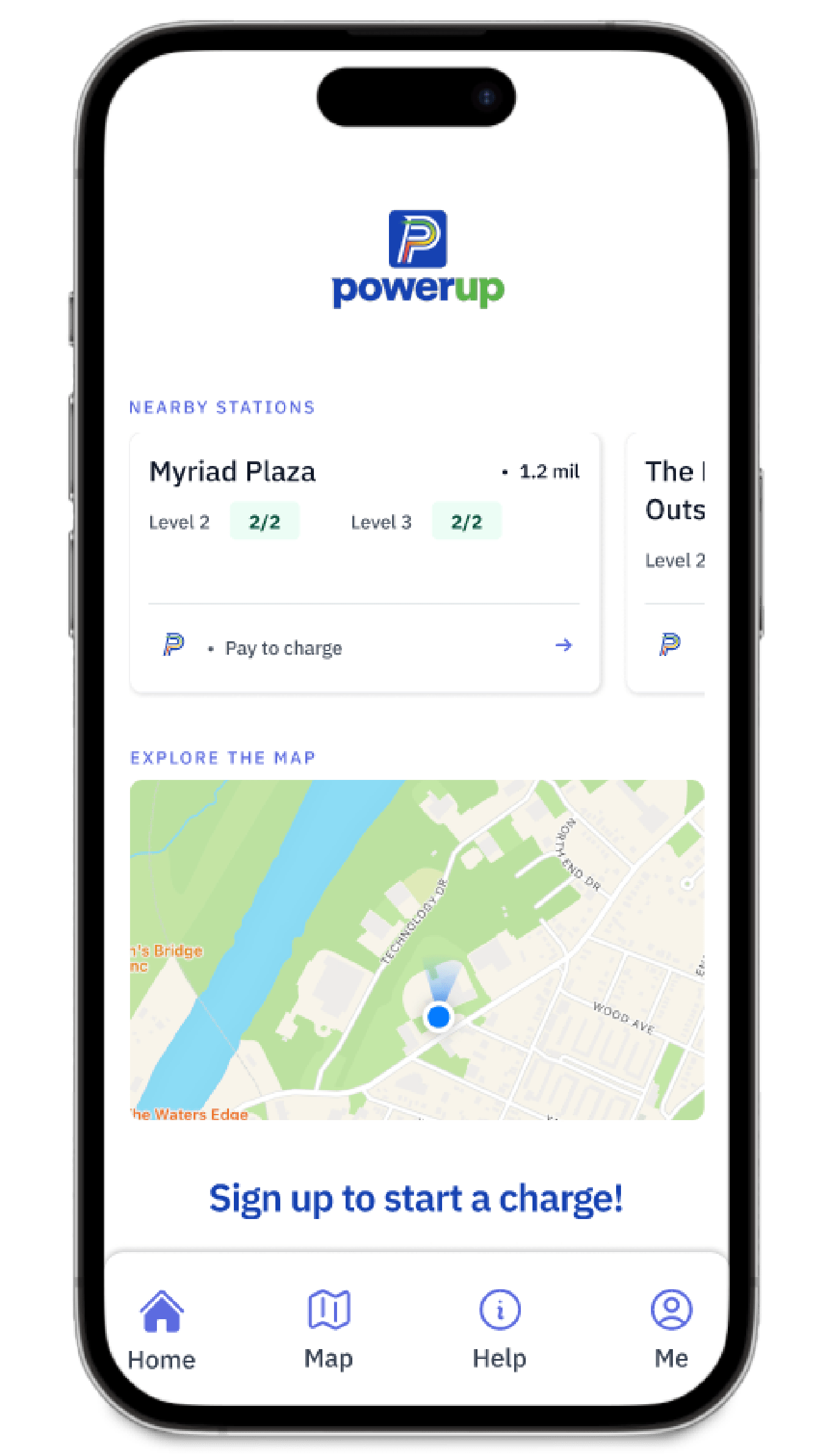
Find a Charger
Locate fast, reliable charging stations near you and power up with ease.
Find a ChargerDownload our Beginner’s Guide to EV Ownership
Get all the tips and tools you need to start your EV journey with confidence.
DownloadPowerUp Newsletter
Stay Up to date on the latest happenings



